4. Suggestions on how to deal with security risks
Security construction should analyze the interests of security threats faced by customers according to the actual situation of users, and build corresponding database security solutions based on the principle of disposing of high risks first, and then disposing of low risks or temporarily not disposing of them. From the perspective of database security operation and maintenance management, operation and maintenance personnel need to protect all database operations from the business level and operation and maintenance level, and combine products and technologies to assist database security operation and maintenance management, and ultimately achieve database security and effective management.
Situation 1: The business system is an intranet system, with many operation and maintenance personnel and many business systems.
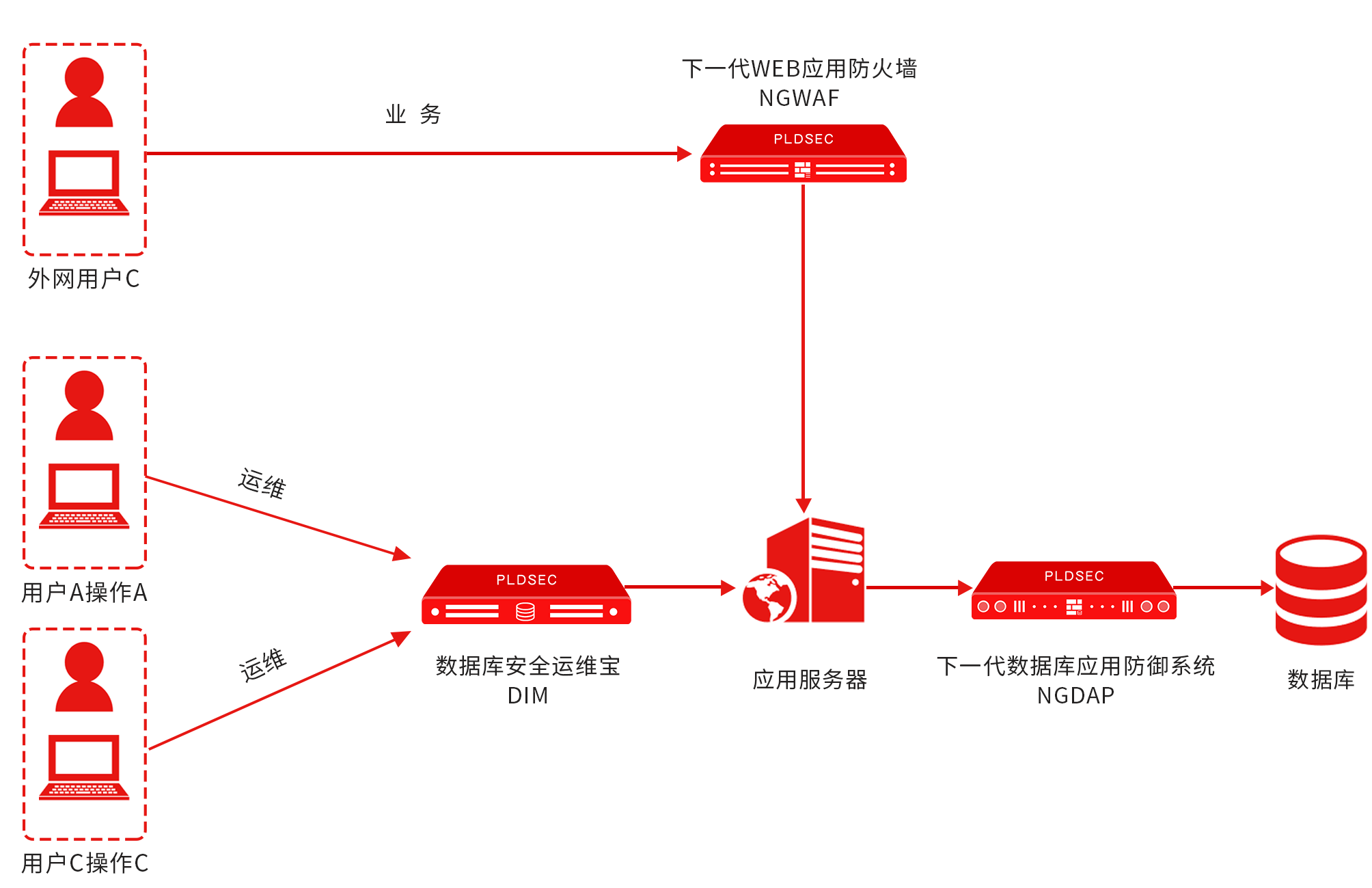
At this time, the risk of directly accessing the database is higher, and the business of indirectly accessing the database is also higher. Comprehensive consideration, you can use the combination scheme of [Palladium database security operation and maintenance treasure DIM combined with Palladium's next-generation WEB application firewall NGWAF] to carry out corresponding security operation and maintenance construction.
Situation 2: The business system is an external network system, there are many operation and maintenance personnel, and there are many business systems.
At this time, the risk of application access to the database and the risk of using tools to access the database are both high. Considering it comprehensively, you can use [Palladium database security operation and maintenance treasure DIM + Palladium database access firewall DAF + Palladium next-generation WEB Application Firewall NGWAF] combined solution to carry out corresponding security operation and maintenance construction.
Scenario 3: Based on the overall security of the current database, it is recommended to provide security protection and real-time interception of dangerous operations.
At this time, the above comprehensive product deployment plan can be used to realize all the pre-warning, inter-blocking, and post-event warning of the database from the operation and maintenance level to the business level.
Conclusion:
When discussing ideas for dealing with database security risks with customers, it is recommended to provide corresponding solutions according to the above different scenarios to ensure that data security risks are minimized to the greatest extent possible.